Machine learning has significant applications in the stock price prediction. In this machine learning project, we are going to build an AI neural network model to predict stock prices. Specifically, we will work with the Facebook's stock.
We will use Yahoo's financial api to download the data and will use scikitlearn and Tensorflow to preprocess and build and train the model. As a disclaimer would like to update here that this is not for investing advice, its purely for fun and learning. You can get the code from here in my GitHub
If you are a beginner and would like to know how Neural networks works then you can refer these two articles
Importing Modules
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
import pandas_datareader as web
import datetime as dt
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense,Dropout,LSTM
Load the Train Data
Here we are using Facebook's data, we can use any other company's ticker symbol to download their data from Yahoo.
#Ticker symbol of the company
company = 'FB'
#Date from which we are collecting the data (year, month, date)
start = dt.datetime(2012,1,1)
end = dt.datetime(2021,1,1)
data = web.DataReader(company, 'yahoo', start, end)
For our model prediction we will use only the Closing price of the Share. Here we are using last 60days of closing price data as window length to predict the next price. There is no hard rule, you can use any length as per your research.
scaler = MinMaxScaler(feature_range=(0,1))
scaled_data = scaler.fit_transform(data['Close'].values.reshape(-1,1))
#How many past days of data we want to use to predict the next day price
prediction_days = 60
#Preparing the Training data
X_train = []
y_train = []
for x in range(prediction_days, len(scaled_data)):
X_train.append(scaled_data[x-prediction_days:x, 0])
y_train.append(scaled_data[x,0])
X_train, y_train = np.array(X_train), np.array(y_train)
#Reshaping so that it will work in Neural net
X_train = np.reshape(X_train, (X_train.shape[0], X_train.shape[1], 1))
Building & Training the model
This is not the only model configuration to train and predict, you can use any combination that suits you best. We can play with different hyperparameter values like number of Neurons, layers, dropouts...
model = Sequential()
model.add(LSTM(units=50, return_sequences=True, input_shape=(X_train.shape[1], 1)))
model.add(Dropout(0.2))
model.add(LSTM(units=50, return_sequences=True))
model.add(Dropout(0.2))
model.add(LSTM(units=50))
model.add(Dropout(0.2))
model.add(Dense(units=1))
model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='mean_squared_error')
model.fit(X_train, y_train, epochs=100, batch_size=32)
Making model predict the existing data
We will test our model to predict the existing data to see how well model is learned
test_start = dt.datetime(2021,1,1)
test_end = dt.datetime.now()
test_data = web.DataReader(company, 'yahoo', test_start, test_end)
actual_prices = test_data['Close'].values
total_dataset = pd.concat((data['Close'],test_data['Close']), axis=0)
model_inputs = total_dataset[len(total_dataset) - len(test_data) - prediction_days: ].values
model_inputs = model_inputs.reshape(-1,1)
model_inputs = scaler.transform(model_inputs)
Preparing it as test data and predicting
X_test = []
for x in range(prediction_days, len(model_inputs)):
X_test.append(model_inputs[x-prediction_days:x, 0])
X_test = np.array(X_test)
X_test = np.reshape(X_test, (X_test.shape[0],X_test.shape[1],1))
predicted_price = model.predict(X_test)
predicted_price = scaler.inverse_transform(predicted_price)
Finally visulaising our predictions
plt.plot(actual_prices, color='black',label='Actual Share price')
plt.plot(predicted_price, color='green',label='Predicted Share price')
plt.title(f"{company} Share Price prediction")
plt.xlabel('Time')
plt.ylabel(f'{company} Share Price')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
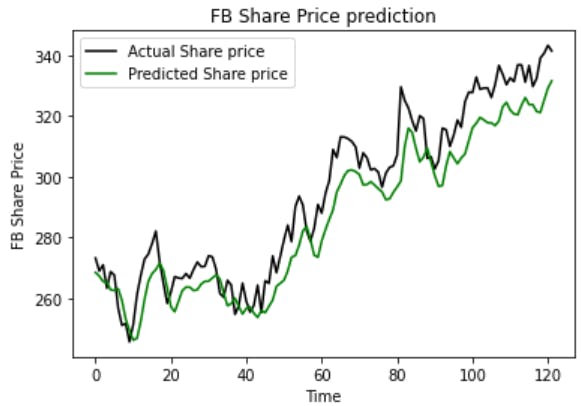
As we can see here with this simple configuration and only with 100 epochs our model is able to follow the actual pattern but the trend value is consistently lower than actual price except very few points where its almost overlapping mean predicted value very close to the actual one.
Predicting the Next Day price
real_data = [model_inputs[len(model_inputs) + 1 - prediction_days : len(model_inputs)+1, 0]]
real_data = np.array(real_data)
real_data = np.reshape(real_data, (real_data.shape[0], real_data.shape[1], 1))
prediction = model.predict(real_data)
prediction = scaler.inverse_transform(prediction)
print(f"Tomorrow's {company} share price: {prediction}")
As per model Facebook's share price will close at $330.63 on 25th June.
Tomorrow's FB share price: [[330.6379]]
The model is trained with 24th June 2021 data and the next day prediction means 25th June value as per model is 330.63 while the actual market closing value for FB's share was 341.17
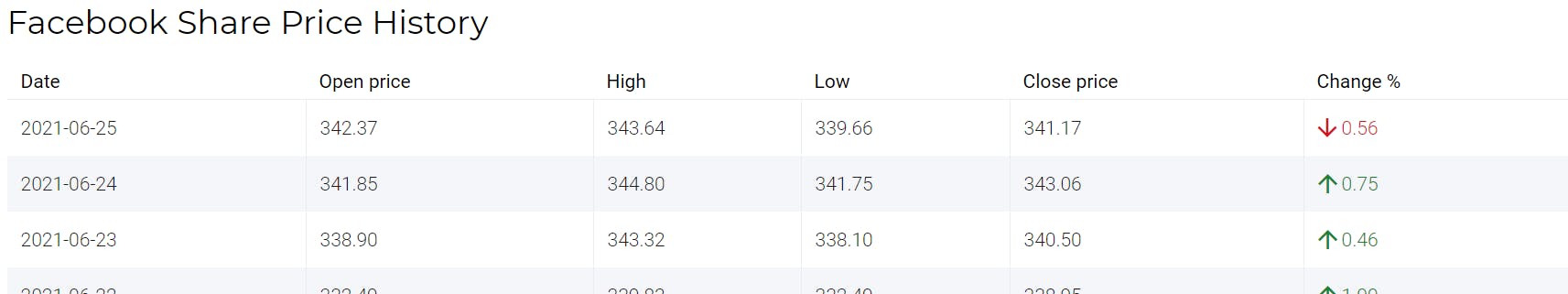
We have error or difference of $11 between actual and predicted value. We can always do more experimentations to reduce that gap and make model more efficient.
You can also try your model and let me know your prediction error on comment section. Happy Learning!