We can generate images from texts by using Zero shot learning(ZSL). It is a technique that uses both observable and non observalble part of the text data for the task. DALL- E mini model is one of such model which uses ZSL to generate images from text input. Its the scaled down version of the OpenAI’s famous DALLE model which recently got a lot popularity in this field. For those who never heard of it DALL·E 2(new version of DALLE) is a new AI system that can create realistic images and art from a description in natural language.For more study you can refer here.
In this blog we will discuss below topics
- Zero-shot Learning?
- How does Zero-shot Text-to-Image generation work?
- Generating image using DALL-E Mini
What is Zero shot learning?
Zero-Shot Learning is a sub field of Transfer Learning as zero-shot learning transfers the knowledge obtained from the training instances to testing instance classification.Usually in recognition models we train the objects with a class labels and during inference when you sent a new target without a label(but associated with one of the training labels) then model try to predict the label of the input image.But in ZSL the goal is to learn intermediate semantic layers and their properties, so that, during inference, a new class of data can be predicted. As an example, a model developed to distinguish between the images of cats and dogs can also identify images of birds. In these instances, the classes covered are known as the “seen” classes, while the unlabelled training instances are called the “unseen” classes.
Knowledge of the seen class can be transferred to unseen classes using a high-dimensional vectorial space called semantic space.. By taking advantage of the semantic space as well as a visual feature representation of image content, ZSL may be solved by projecting the visual feature vector and prototype into a combined embedding space. The projection of an image feature vector is matched to the unseen class by using the Nearest Neighbour Search (NNS).
To read more about ZSL please refer this amazing blog from analytics india.
How ZSL perform the text to image generation?
Here the ZSL’s goal is to maximise the Evidence lower bound(ELB) or sometimes called variational lower bound or negative variational free energy on the joint likelihood of the model distribution over images, the description of the image, and the tokens for the encoded RGB image.
Evidence Lower Bound is the statistical technique to approximate the log-likelihood function. It is a part of variational Bayesian inference. So Evidence here is the log-likelihood function and Lower Bound is the method which helps to approximate the function. If pixels were used directly as image tokens, high-resolution images would require too much memory. The likelihood objective tends to prioritise modelling short-range dependencies between pixels, so much of the modelling capacity would be dedicated to recording high-frequency details, rather than developing the low-frequency structure that makes objects visually recognisable.
Training Discrete Variational AutoEncoder
Each RGB image is compressed by a discrete variational autoencoder (dVAE) into smaller image tokens, each element of which can assume thousands of possible values. This reduces the context size of the transformer without a large degradation in visual quality and it fastens up the process of training. This process is just like how we can label different things from a distant location even if it is not in a clear vision because we have trained our mind to recognize just by seeing the outline and gradients of things. Now we need to set the initial before the uniform categorical distribution over the possible value codebook vectors, and these vectors need to be parameterized at the same spatial position as the smaller image output by the encoder. The Evidence Lower Bound (ELB) now becomes difficult to optimize, as the initial prior becomes a discrete distribution.
So, we need to convert the categorical distribution into continuous distribution by refactoring the sample into a deterministic function of the parameters and some independent noise with the fixed distribution this process is also called relaxation. For performing this kind of operation Gumbile trick is perfect. Once the temperature factor of Gumbile one hot vector encoding tends to infinity the distribution starts to become uniform. Now, the exponentially weighted iterate averaging is utilized to maximize relaxed ELB. The likelihood for the distribution over the RGB images generated by the dVAE decoder is evaluated using the log-Laplace distribution.
The cross-entropy losses are to be normalised for the text and image tokens by the total number of each kind in a batch of data. Since we are primarily interested in image modelling, we multiply the cross-entropy loss for the text by 1/8 and the cross-entropy loss for the image by 7/8.
Prior Learning
This step focuses on the concatenation of text tokens encoded with the smallest converted image tokens and forms the learner with an auto regressive transformer.
To encode text-image, Byte-Pair Encoding (BPE) is used which encodes the lower cased descriptions and the image using tokens with vocabulary. To ensure that words that often appear in the vocabulary are assigned to one token, the rarer words are broken down into several tokens. As described earlier, the dVAE encoder logit is used to generate image tokens.Then the text and image tokens are concatenated and modelled auto regressive as a stream of data.
It uses a transformer with 12 billion sparse parameters that learns the prior distribution over the text and image tokens by maximising the ELB.
Generating image using DALL-E Mini
We will be using DALL-E mini a pretrained model from Hugging face that works on ZSL for generating images from text descriptions.
NOTE: Based on the experience its my recomondation to either use the Google collab or setup with more than 8GB RAM and a good amount of CPU cores to test this otherwise you machine may crashes or forcefully the kill the kernel due to CPU or Memeory exhaust.
Installing the Prerequistes
We are basically installing a transformer, vqgan-jax and dalle-mini model.
Loading the Model and Tokeniser
- dalle·mini for text to encoded images
- QGAN for decoding images
- CLIP for scoring predictions
The Vqgan model will generate tokens for the description and the images and the Clip model will calculate the scores for the image generated. Here we are using WANdb API, you will need a key to use this API which could be easily be generated from the wandb.ai. You just need to signup and it will generate an API token for your profile.
Generating Images
You can set below parameters for image generation based on your requirements. Higher the temperature the model tried higher to be more innovative and generate more realistic image that are closer to the text input. You can play with various combinations and try different samples.
Below are few examples of the generated images from my machine.
Image-1
Its a less complex text and seems model did a pretty good job on image creation which looks quite closer to the input description but still the dog legs are looking weirdly aligned.
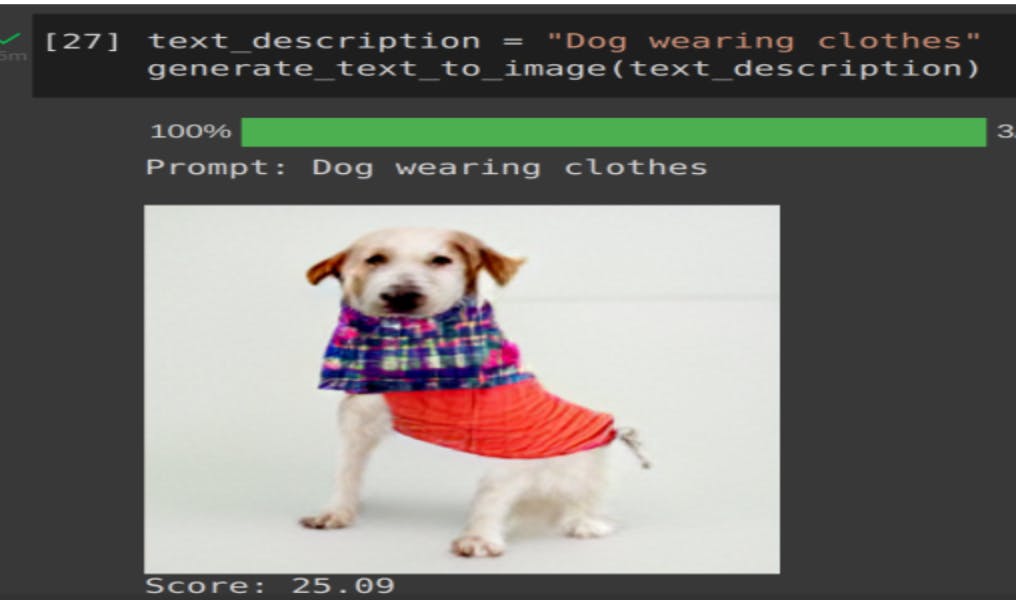
Image-2
This one more complex text compared to the previous one and we can see model failed to generate the accurate image. It was able to create a swimming pool but no sign of astronaut.
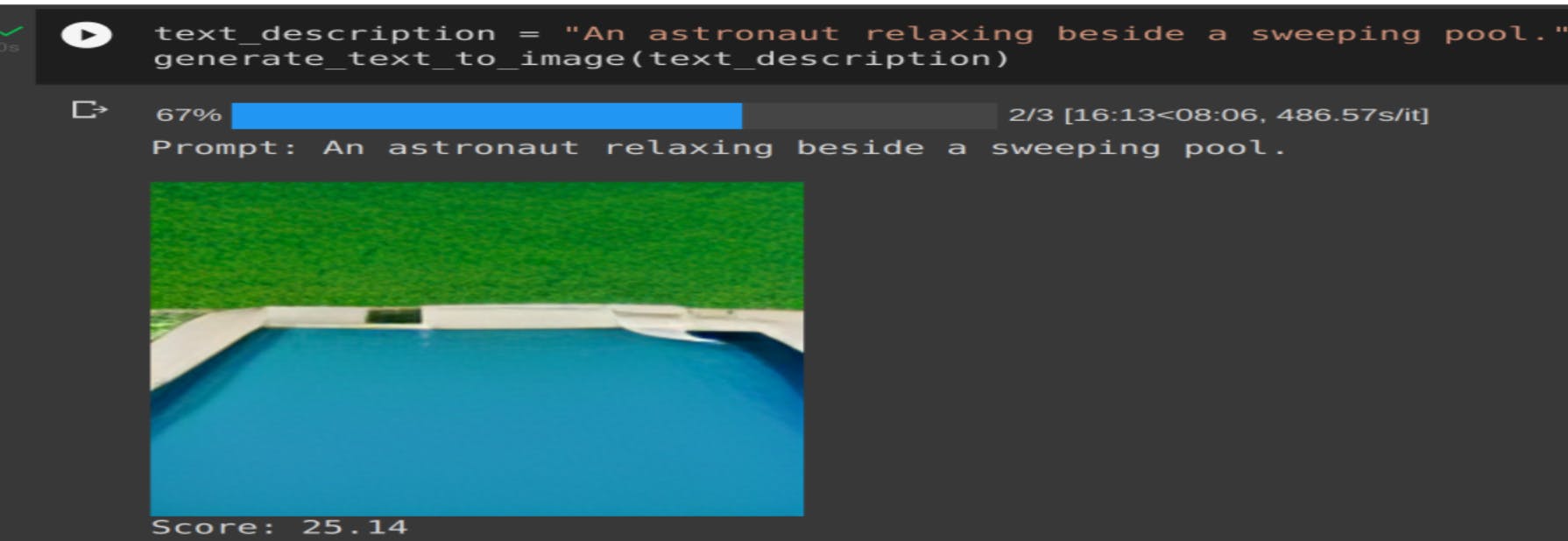
Image-3
Looks like its trying to merging the face of both human and cat.
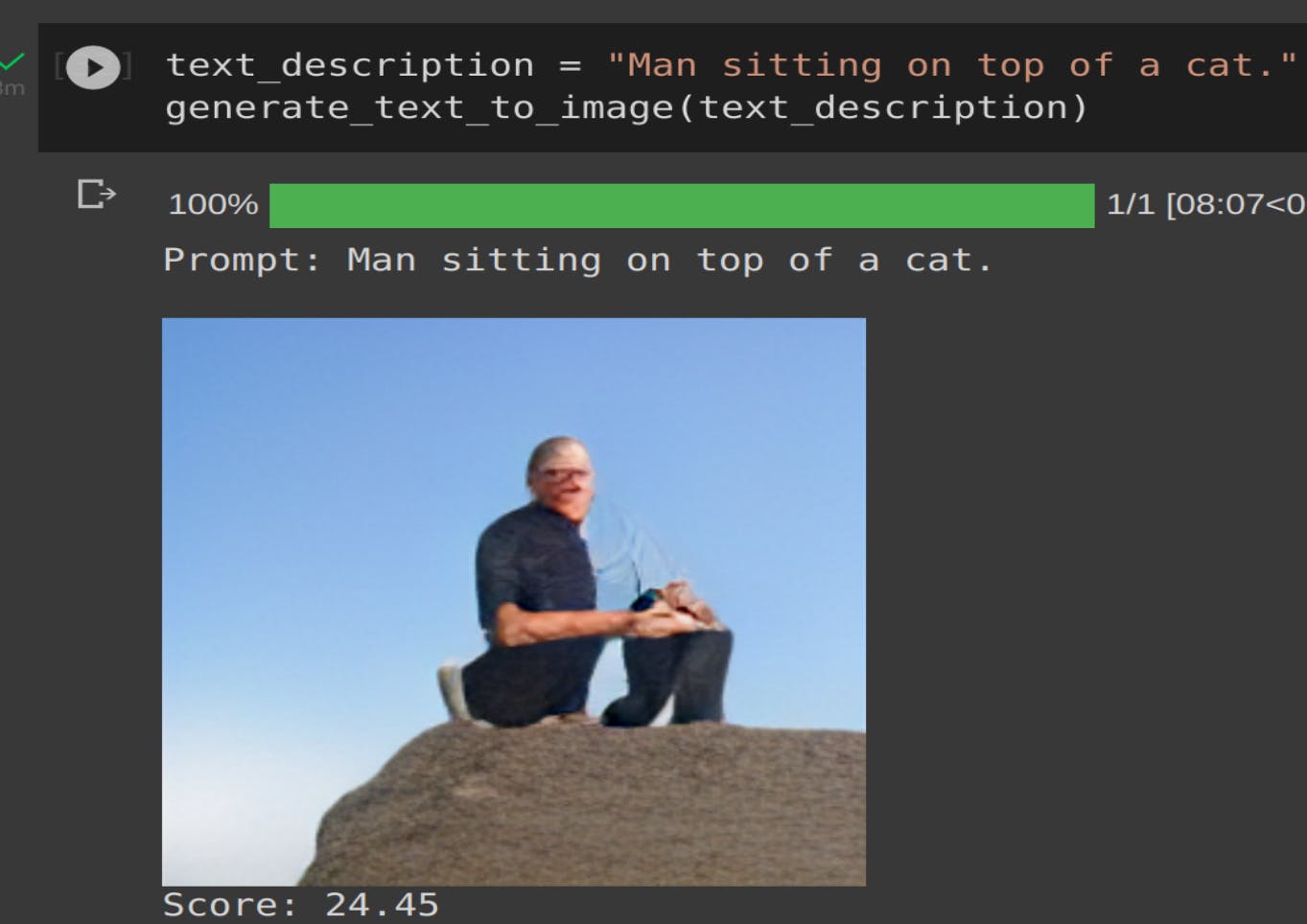
Image-4
It’s able to generate a cat image but failed to fit the hat. The face of cat is also somewhat misaligned. Not sure which direction cat is looking.
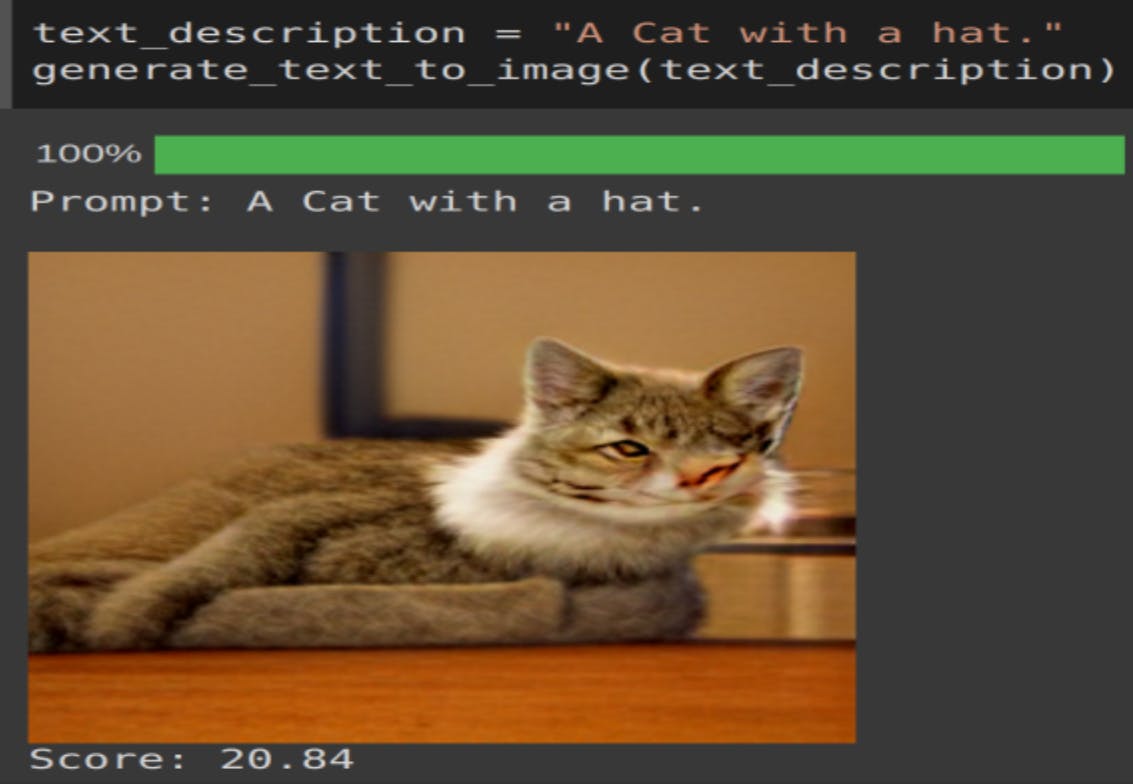
Conclusion
The implementation of Zero-Shot Learning in the Text-to-Image generation proved to be an excellent solution for the challenges encountered when synthesising images. The models are based on less data and the predictability of the images is remarkable. This article provides knowledge of ZSL and how it is used to synthesise pictures from textual descriptions, as well as an implementation of python theory.Have fun with experimenting it. You can find the full code here.
Hope you have enjoyed the blog. Happy Learning!!
